Natoma Blog
How To: Enabling MCP in Claude Desktop
Jun 16, 2025
Pratyus Patnaik
Claude Desktop is a powerful LLM client by Anthopic, designed for both personal and professional use. By integrating it with a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, you can dynamically inject real-time, relevant context into your Claude sessions from documents, workspaces, tools, apps, and data sources. You can also enable Claude to go beyond text or image generation, taking direct action in business systems like Slack, Salesforce, Jira, and more.
This step-by-step guide will walk you through three methods for integrating Claude Desktop with an MCP server using the examples of GitHub, Asana, and Datadog.
MCP Server Types Supported
Claude Desktop supports the following types of MCP servers:
Local Stdio: Runs on your machine and streams responses via standard input/output (stdio).
Streamable HTTP: The server operates as an independent process that can handle multiple client connections
Step 1: Enable MCP in Claude Desktop
Open the Claude Desktop App.
Click Developer in the left-hand sidebar.
Click Edit Config.
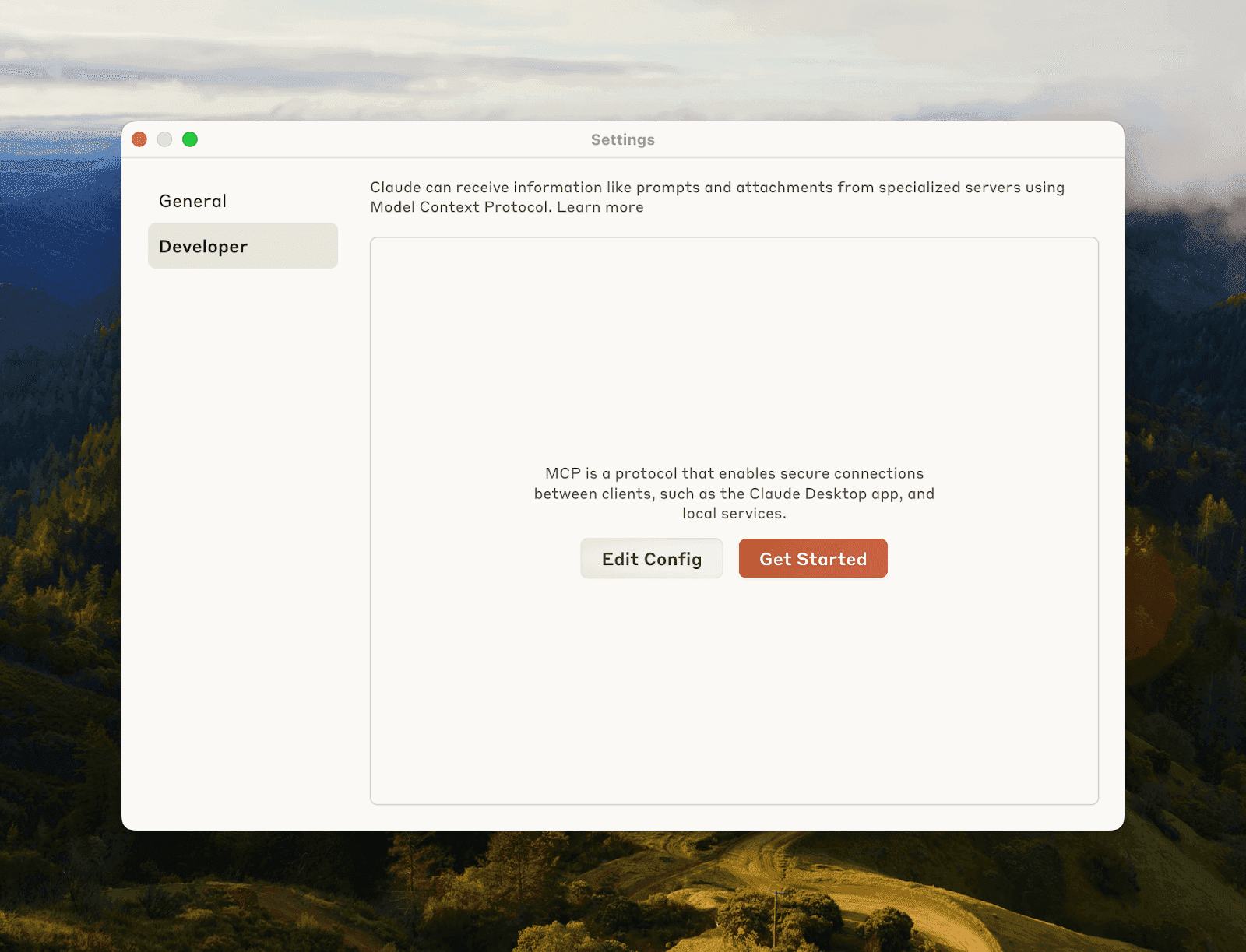
This will create or open the config file at one of the following paths:
Add or modify your configuration as shown in the examples below.
Step 2: Choose Your MCP Server Setup
Claude Desktop requires an MCP-compliant server that can respond to context queries. You have three setup options:
Option A: Run the MCP Server Locally
Ideal for development, testing, and debugging.
Instructions:
Install Docker.
Ensure Docker is running.
If you encounter issues pulling the image, try running `docker logout ghcr.io` to refresh your credentials.
Create a GitHub Personal Access Token.
Choose permissions based on what you’re comfortable sharing with the LLM.
Learn more in the GitHub documentation.
Config Example:
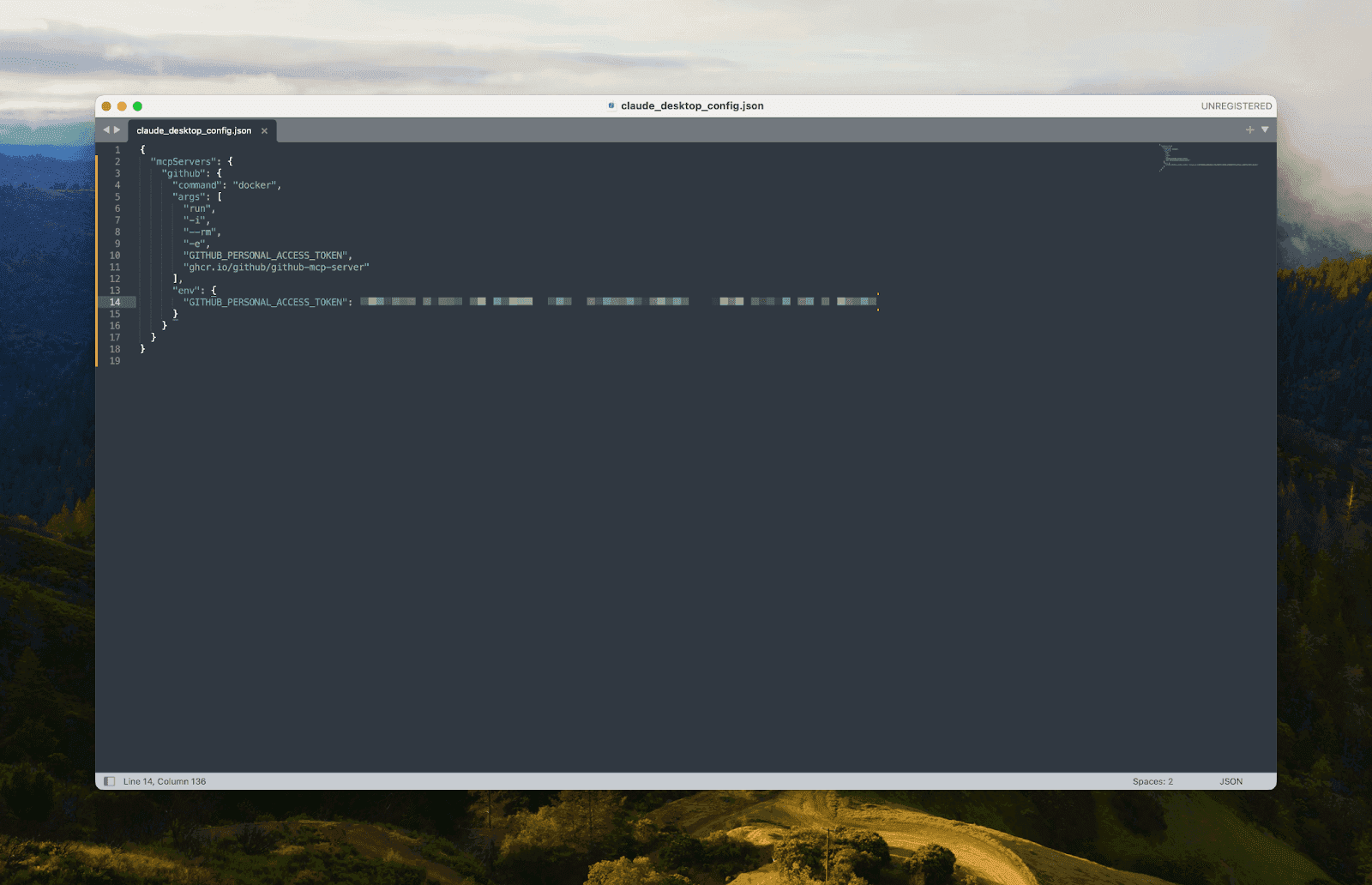
Save and restart Claude
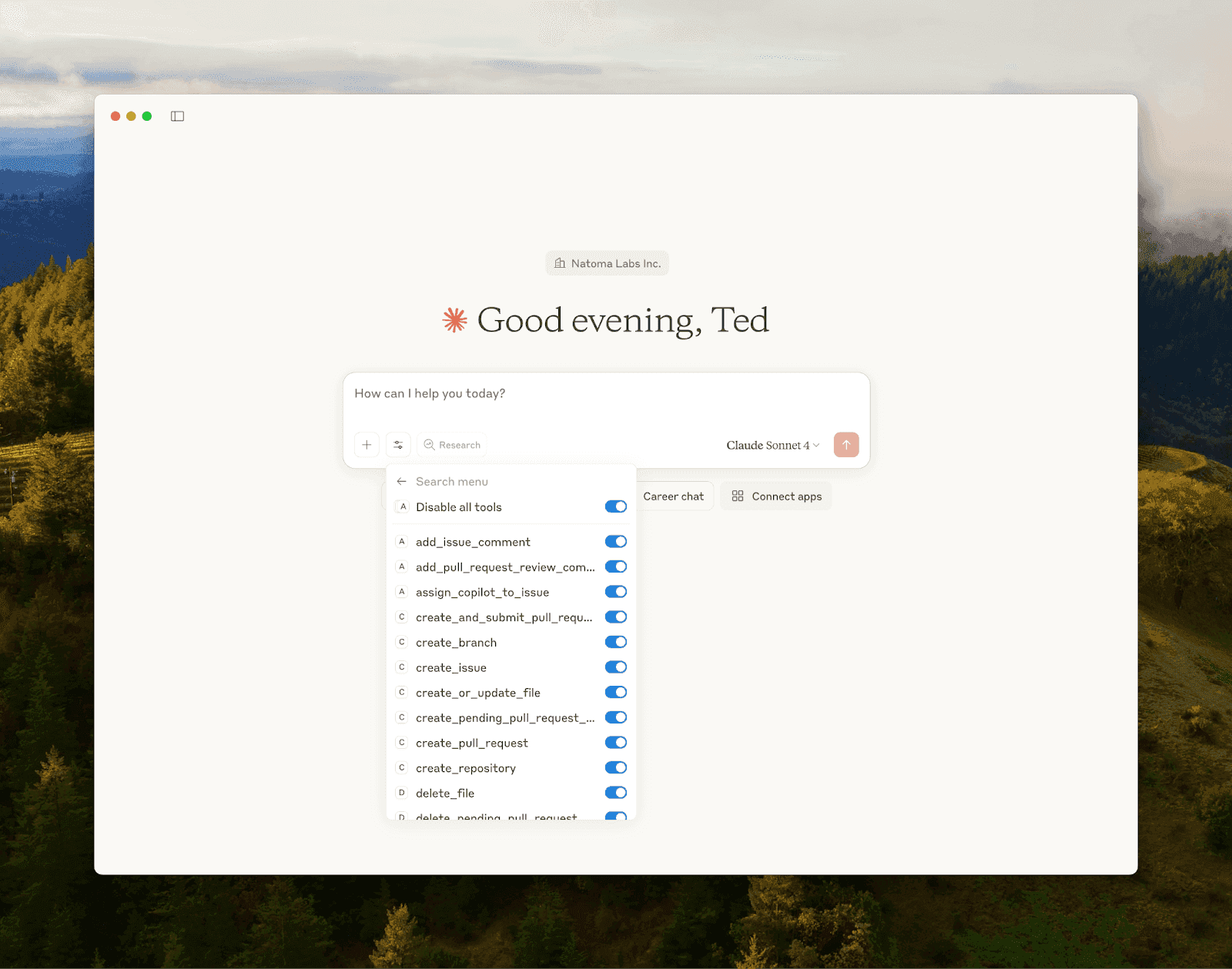

Option B: Use a Hosted MCP Server (e.g., Asana, Atlassian)
The easiest option—no setup required. Note that you won’t have central control or visibility into interactions between Claude and the integrated service.
Method 1: Via UI
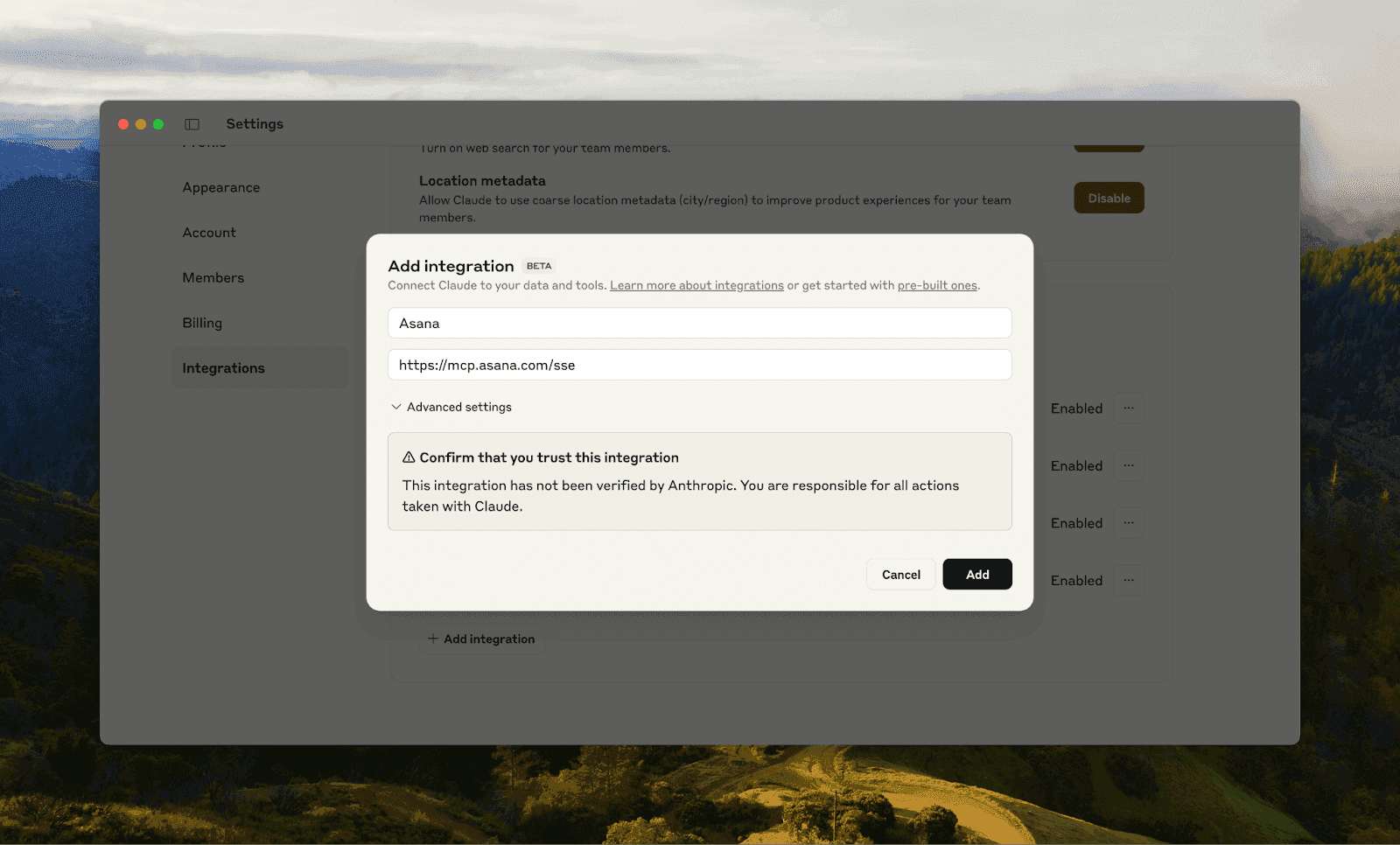
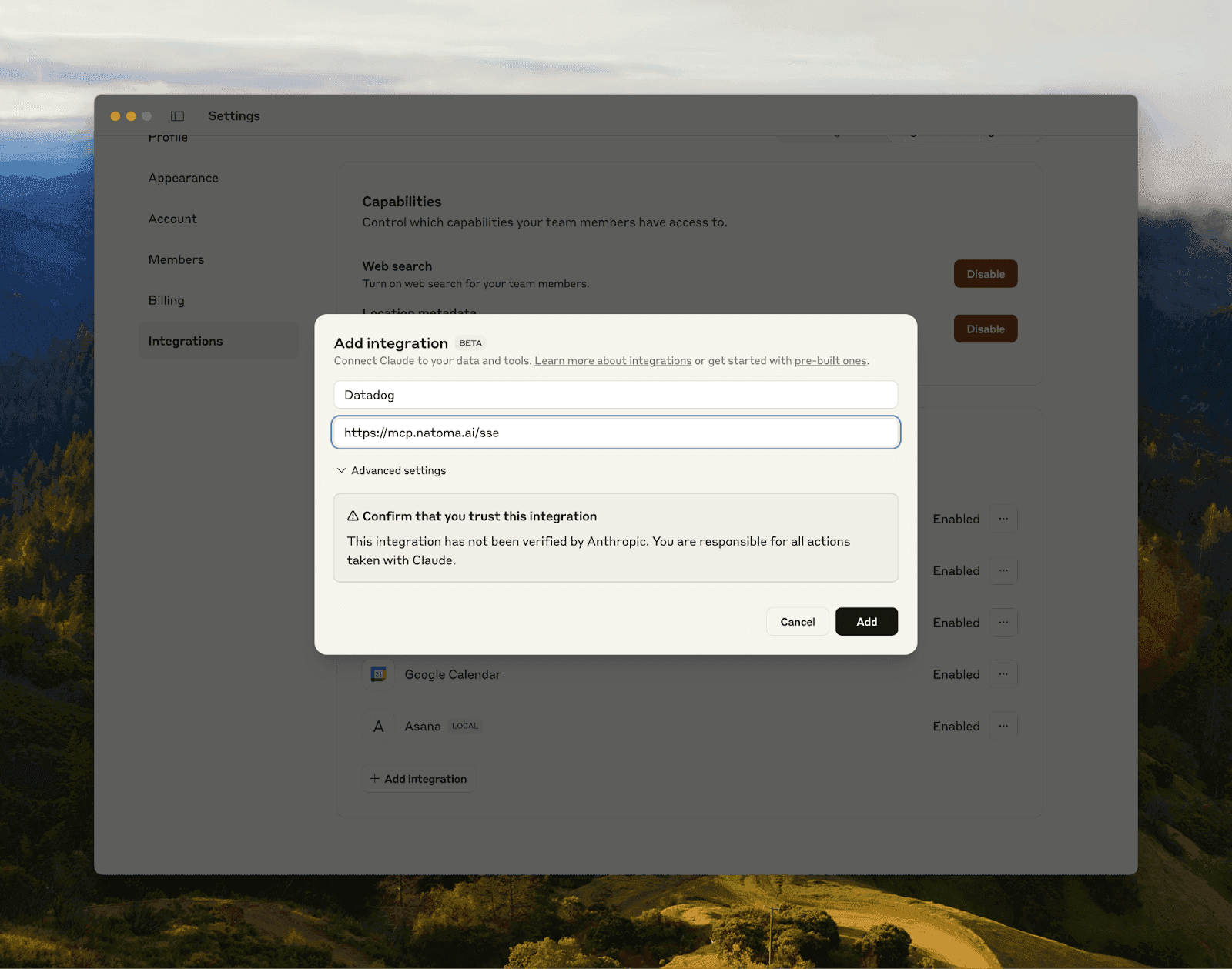
Navigate to Settings > Integrations.
For Enterprise or Team plans, go to the Organization integrations tab.
Click Add integration.
In the modal:
Integration name: Any label (e.g., Asana)
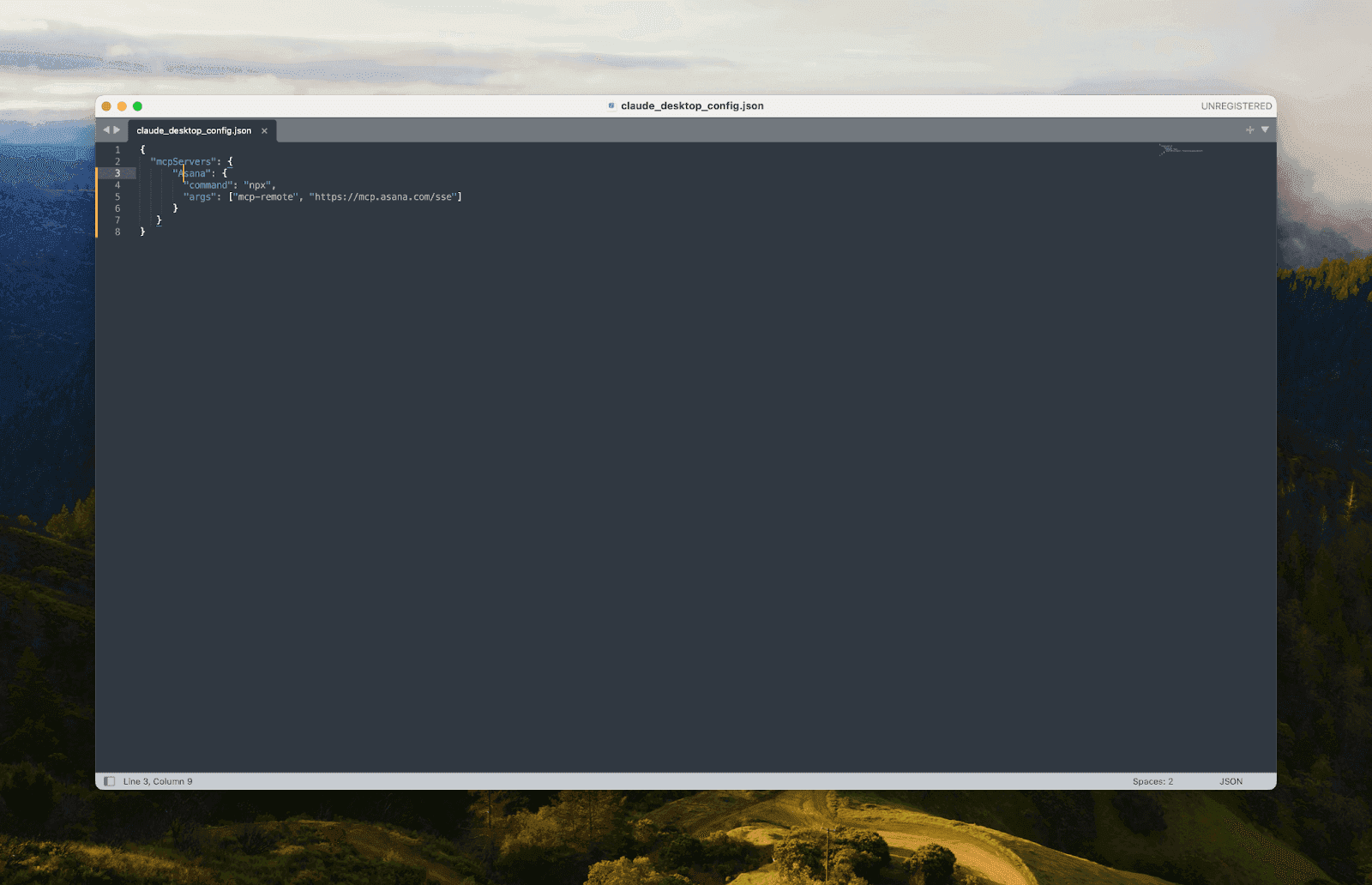
Integration URL: For Asana, use `https://mcp.asana.com/sse`
Click Add, then Connect to authenticate.
Method 2: Via Config
Install the `mcp-remote` package.
Config Example:
Save and restart Claude

Option C: Deploy Your Own Remote MCP Server
Recommended for teams and production use. This setup offers:
Full visibility and governance
Access control across employees and agents
You can deploy your MCP server using a platform like Natoma. Connect apps from the registry, and retrieve the configuration
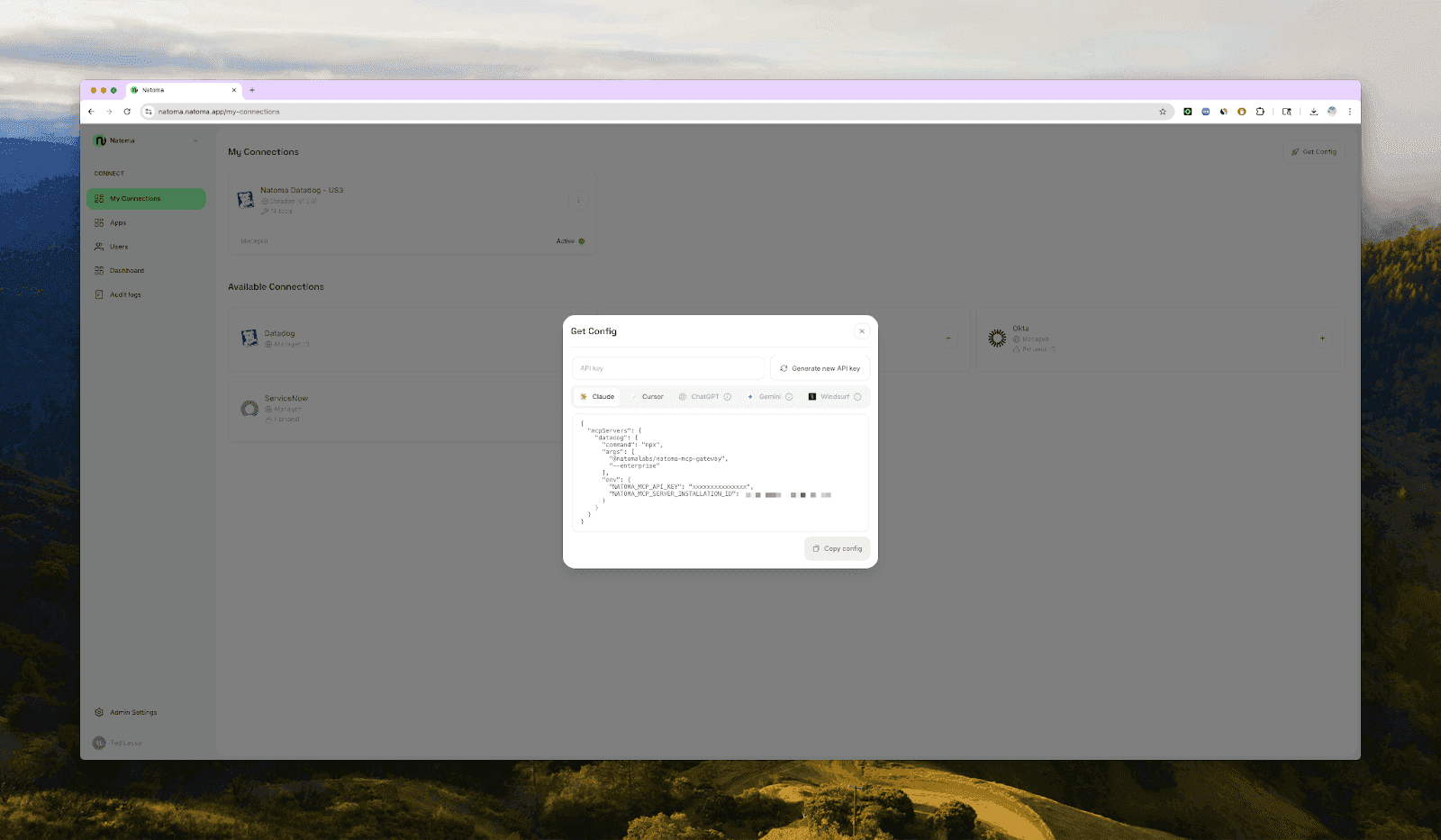
or Streamable HTTP endpoint, and paste it into Claude Desktop.
Restart Claude
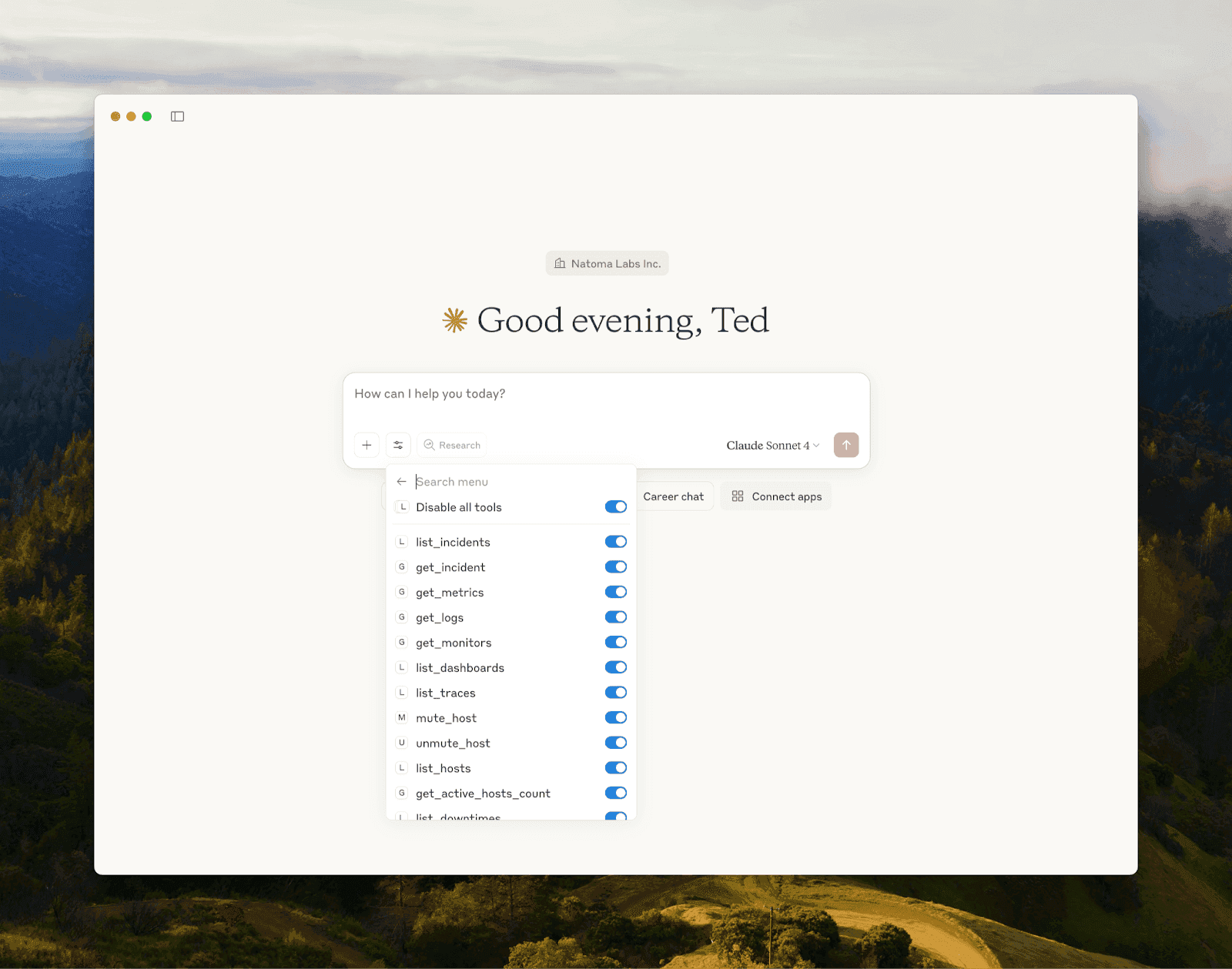

Troubleshooting & Testing
To verify MCP integration:
Ask Claude a question that requires context from recent activity.
Claude will send a background request to the MCP server, which returns structured context.
Monitor Claude MCP logs at:
Claude may block localhost URLs depending on CORS policies. Use ngrok or a Cloudflare Tunnel for HTTPS tunneling.
Ensure your MCP server responds with valid JSON in the correct schema.
Use the MCP Inspector for debugging.
Wrap-Up
Integrating Claude Desktop with an MCP server—whether local, remote, or SaaS-hosted—takes just a few steps, but can have varying degrees of complexity. Using tools like Natoma can help streamline the process and ensure that security controls are covered. The result is a significantly enhanced contextual experience, making your interactions with Claude more powerful and personalized. Claude more powerful and personalized.



